Project Overview
What is Alpha Thalassaemia?
Thalassaemia is passed from parent to child in genes. Genes carry information about human characteristics such as eye colour, hair colour and haemoglobin. Thalassaemia is inherited. Thalassaemia is not contagious. Thalassaemia is not transmitted by germs.
Sometimes changes occur to genes, resulting in medical conditions. Such changes occur to alpha globin genes in Alpha (a) Thalassaemia:
- A person normally inherits four alpha globin genes for the production of the alpha globin protein in haemoglobin.
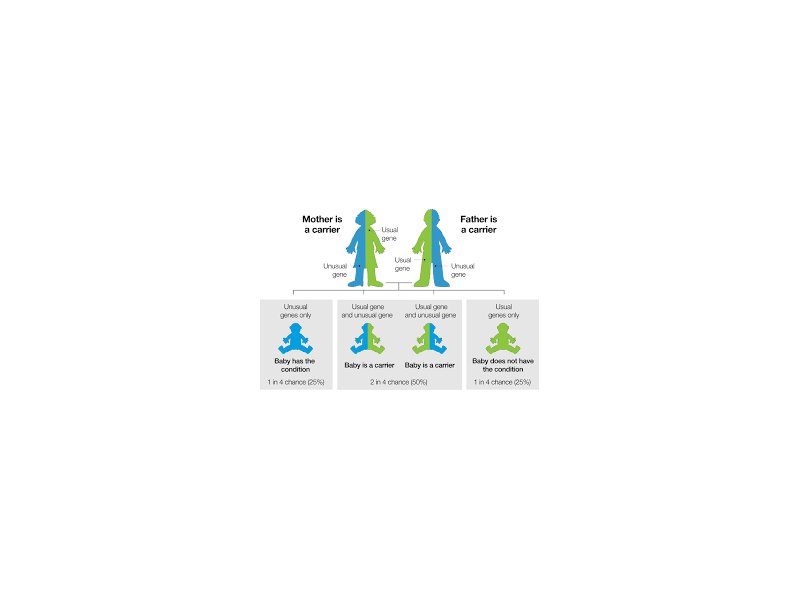
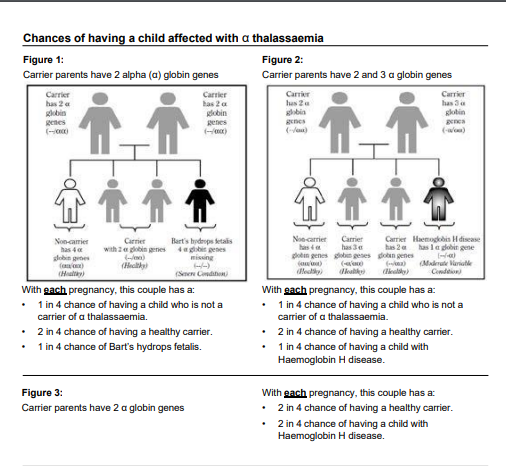
- A person may have two or three of the normal four alpha globin genes for haemoglobin production. This person is called a carrier of a Thalassaemia and is healthy.
- Carriers may be at risk of having a child affected with Haemoglobin H Disease or Bart’s Hydrops Fetalis if their partner is also a carrier of certain types of a Thalassaemia.
- When a person has only one alpha globin gene, they have Haemoglobin H Disease and require regular medical care. Individuals with Haemoglobin H Disease may experience lifelong anaemia of mild to moderate degree. Occasionally it may be severe.
- When a person has no alpha globin genes, they have a severe condition called Bart’s Hydrops Fetalis. Bart’s Hydrops Fetalis affects a foetus long before birth, resulting in death during pregnancy or shortly after birth. This is a fatal condition which is dangerous for both the mother and baby during pregnancy.
What is Beta Thalassaemia?
Thalassaemia is passed from parent to child in genes. Genes carry information about human characteristics such as eye colour, hair colour and haemoglobin. Thalassaemia is inherited. Thalassaemia is not contagious. Thalassaemia is not transmitted by germs.
Sometimes changes occur to genes, resulting in medical conditions. Such changes occur to beta globin genes in Beta (b) Thalassaemia:
- A person normally inherits two beta globin genes for the production of the beta globin protein in haemoglobin.
- A person may have an alteration (mutation) in one of their two beta globin genes. This person is called a carrier of b Thalassaemia and is healthy. Doctors may use the term b Thalassaemia minor instead, but it means the same thing.
- Carriers may be at risk of having a child affected with Beta Thalassaemia Major if their partner is also a carrier of b Thalassaemia.
- When a person has alterations (mutations) in both of their b globin genes, they have a severe condition called b Thalassaemia Major. Beta Thalassaemia Major results in severe anaemia requiring lifelong treatment.